Malaria is a parasitic infection spread to humans by female Anopheles mosquitoes. The single-celled parasites are in the genus Plasmodium. Typically, four kinds of malarial parasites infect humans, Plasmodium falciparum, P. vivax, P. ovale, and P. malariae. P. Knowlesi, a type of malaria that naturally infects macaques in Southeast Asia, may also infect humans, causing malaria that is transmitted from animal to human.
Treatment for H. pylori infection involves taking a combination of antibiotics and a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) to reduce the amount of acid in the stomach (acid suppression). Most people do not need to be tested for H. pylori if they do not show signs of infection.
Marburg virus is the causative agent of Marburg virus disease (MVD) formerly known as Marburg haemorrhagic fever. MVD is a zoonotic infection, transmitted from animals to humans. It is a highly virulent disease that causes hemorrhagic fever with an 88% fatality rate. The virus can spread by human-to-human contact with blood, body fluids and by contact with infected body fluid objects.
Noroviruses are the most common cause of acute gastroenteritis (stomach flu) in humans, accounting for more than 60% of cases. It affects people of all ages, but it causes severe acute gastroenteritis in children under the age of five. Norovirus is the most common cause of illness and outbreaks due to contaminated food.
Multidrug resistant TB (MDR TB) is a disease caused by any strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis which is not effectively killed by both isoniazid and rifampin, two of the first-line, safest and most effective anti-TB medications.
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a very common virus that causes infections of the respiratory tract. Other than monitoring for symptoms, most used RSV are diagnosed clinically. Most RSV infections go away on their own in 1-2 weeks.
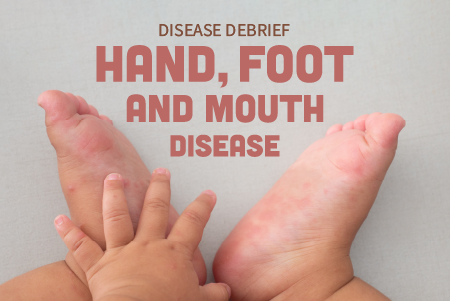
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) is a highly contagious disease caused by a virus belonging to Enteroviruses. Symptoms usually include fever, mouth sores, and a skin rash commonly found on the hands and feet.
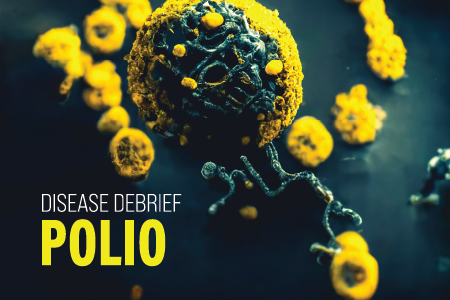
Polio is a highly contagious, vaccine-preventable disease, most often seen in children under 5 years of age. Transmission of polio is person-to-person, mainly through the fecal-oral route and less frequently via contaminated water or food.
West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne disease caused by a positive, single-stranded RNA virus belonging to the genus Flavivirus. Found in Africa, Europe, the Middle East, West Asia, and North America, WNV is maintained in an enzootic cycle involving a mosquito-bird-mosquito transmission.
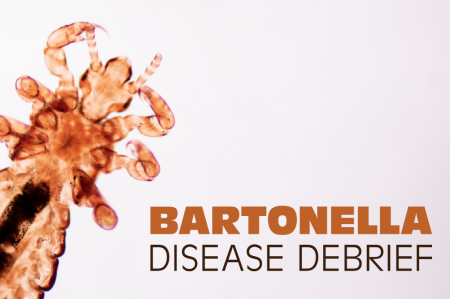
Bartonellosis is a group of infectious diseases caused by bacteria within the Bartonella genus. The bacteria are fastidious, aerobic, gram-negative cocci/small rods, and are hemotropic. The bacteria invade erythrocytes and the lining of blood vessels where they then proliferate.
Blastomycosis is a pulmonary, cutaneous or disseminated infection caused by the fungus Blastomyces dermatitidis (B. dermatitidis). This fungus exists in mold form in the environment; it produces microscopic fungal spores, particularly in moist soil and in decomposing matter such as wood and leaves.
Ignatzschineria indica (I. indica) infection is caused by myiasis, the infection of human tissue by fly larvae. It is transmitted by the larvae (maggots) of flesh flies (Sarcophaginae) and blow flies (Calliphoridae).