Mpox virus (formerly Monkeypox) is a zoonotic, double-stranded DNA virus, which also includes the variola virus (smallpox), cowpox virus, and vaccinia virus.
Recent research has reclassified the mpox virus into two distinct clades, now officially referred to as Clade I (formerly the Central African or Congo Basin clade) and Clade II (formerly the West African clade).
Shigellosis is an acute, invasive, enteric bacterial infection that affects the digestive system. It is caused by a group of bacteria called Shigella. Symptoms may appear within 1–2 days of encountering Shigella.
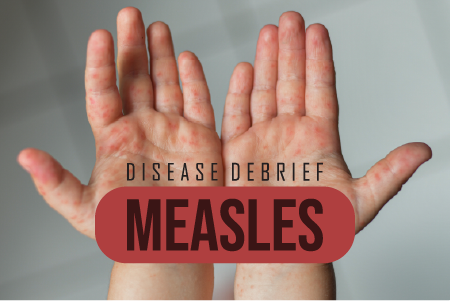
Measles is a single stranded, enveloped RNA virus. The virus can cause a measles infection which starts in the respiratory epithelium of the nasopharynx. Measles is highly contagious. Complications from measles commonly include ear infections and diarrhea.
H5N1 AI is a highly pathogenic avian influenza virus that is easily transmitted between birds and is a zoonotic disease (a disease that transmits from animals to people), but it is not well adapted to mammals. There have been reports of possible limited human-to-human transmission, but there has been no evidence of ongoing transmission between people.
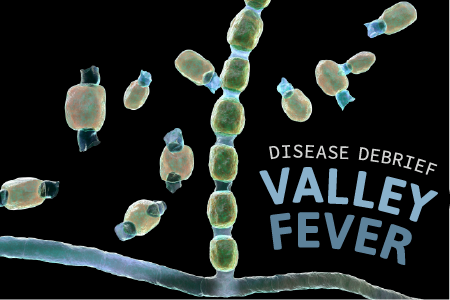
Valley fever (also known as coccidioidomycosis) is a lung infection caused by two species of the fungus Coccidioides. The Coccidioides fungus can be found in semiarid soils of the Pacific Northwest and Southwestern United States, Mexico, Central America, and South America.
Congenital syphilis is a sexually transmitted bacterial disease passed from mother to child during pregnancy or birth. When left untreated, syphilis in pregnant women can cause serious health consequences including miscarriage, stillbirth, neonatal death, or birth defects. Congenital syphilis is re-emerging and has risen significantly in recent years. In 2019, for example, there were 53 cases of congenital syphilis, the highest number of cases ever reported in Canada. Case counts have risen significantly since 2019 in the provinces, although numbers for the country as a whole are not yet available.
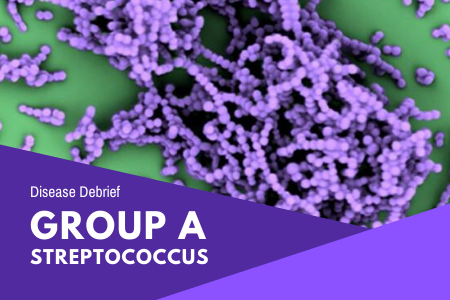
Group A streptococcus (GAS) is responsible for a range of diseases in humans. These diseases include strep throat (acute pharyngitis) and skin and soft tissue infections such impetigo and cellulitis. These can also include rare cases of invasive (serious) illnesses such as necrotizing fasciitis (flesh eating disease) and toxic shock syndrome (TSS).
Treatment for H. pylori infection involves taking a combination of antibiotics and a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) to reduce the amount of acid in the stomach (acid suppression). Most people do not need to be tested for H. pylori if they do not show signs of infection.
Noroviruses are the most common cause of acute gastroenteritis (stomach flu) in humans, accounting for more than 60% of cases. It affects people of all ages, but it causes severe acute gastroenteritis in children under the age of five. Norovirus is the most common cause of illness and outbreaks due to contaminated food.
Multidrug resistant TB (MDR TB) is a disease caused by any strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis which is not effectively killed by both isoniazid and rifampin, two of the first-line, safest and most effective anti-TB medications.
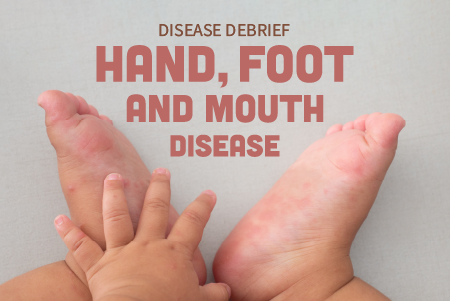
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) is a highly contagious disease caused by a virus belonging to Enteroviruses. Symptoms usually include fever, mouth sores, and a skin rash commonly found on the hands and feet.
Polio is a highly contagious, vaccine-preventable disease, most often seen in children under 5 years of age. Transmission of polio is person-to-person, mainly through the fecal-oral route and less frequently via contaminated water or food.